More than 4 million babies are born in the United States each year, many to mothers who live with chronic illness. Historically, pregnant women are excluded from research, consequently there is limited to no safety data at the time of drug approval. Enormous gaps remain regarding the clinical impact of exposure to biologics and medications when so much is at stake for both mom and baby. July 11-12th the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) hosted a public workshop entitled, “Evaluating Immunosuppressive Effects of In Utero Exposure to Drug and Biologic Products.”
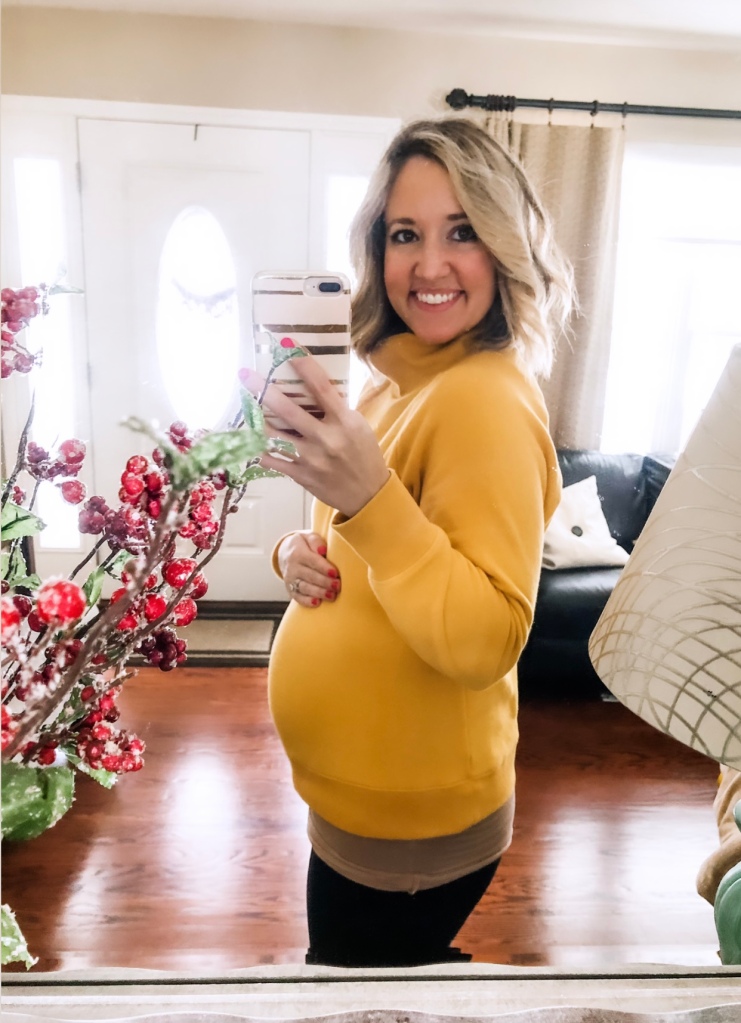
As a patient leader in the IBD community and mom of three children who were all exposed to anti-TNF medication in pregnancy, I was invited to provide the patient voice during this two-day discussion. I spoke on three different panels to share my perspective. This week on Lights, Camera, Crohn’s I’ll share what I learned and what I heard from top researchers and doctors at the workshop. The key overall message—healthy moms lead to healthy babies and a healthy society. Healthy meaning—having disease well-controlled in pregnancy so flares don’t lead to adverse outcomes for both mom and baby.

Pregnant women and lack of research
Often due to ethics, pregnant women have been omitted from research and clinical trials. The absence of human involvement in pharmacology studies can lead to uncertainty about what is deemed “low risk” and “safe” to the fetus, and the impact medications have on the placenta. Women who become pregnant must drop out of clinical studies, even if the drug class has known safety or is deemed low risk (anti-TNF, IL-23s).
According to study entitled, “Medication use during pregnancy with a particular focus on prescription drugs”, Pregnant women report taking an average of 2.6 medications at any time during pregnancy. Medication use may expose the fetus and infant to the medication through placental transfer.
It’s clear that reducing or stopping medications can put mothers at risk for flares, which in turn can lead to adverse effects in pregnancy. With my own children, I stayed on Humira until 39 weeks with my oldest (who is now 7), and 37 weeks with my other two children (who are now 5 and 3). All three of my children were a part of pregnancy studies (MotherToBaby and PIANO). My youngest will be followed until age 18! My oldest was followed through kindergarten. The current recommendation, globally (which has changed since I had my children) is to keep women on biologics throughout the entire pregnancy.

One of the key areas of discussion is whether animal data from research ever tells us the whole story about the safety and efficacy of medications—the answer is no. There is no substitute for a human placenta, but the challenge and dilemma are what can be done to get this human data. Approaching clinical trials in pregnant women is challenging and takes time to develop. Currently, animals are the best tool we have for educated guesses.
The benefit vs. risk discussion for Mom and Baby
Oftentimes decision making with chronic illness is a risk versus benefit thought process, whether you are pregnant or plan to carry a baby in the future or not. During the FDA workshop, there was an incredible presentation that really resonated with me about the multiple decisions women have to make for both themselves and their unborn children. The discussion highlighted the complexity and why it’s not a black and white decision. These series of decisions are nested in each other and revolve around the decision maker (Mom/Dad) and medical providers.
Key considerations we deal with as IBD moms:
Continue or discontinue medication?
Should we breastfeed on medication?
Should we give an attenuated live vaccine as scheduled or delay?

When making these decisions it’s imperative that patients feel heard and that communication take place between the parents and medical providers (gastroenterologist, maternal fetal medicine, and OBGYN). Knowledge is power and educating yourself going into these conversations and before and during pregnancy can make you feel more empowered in your decisions.

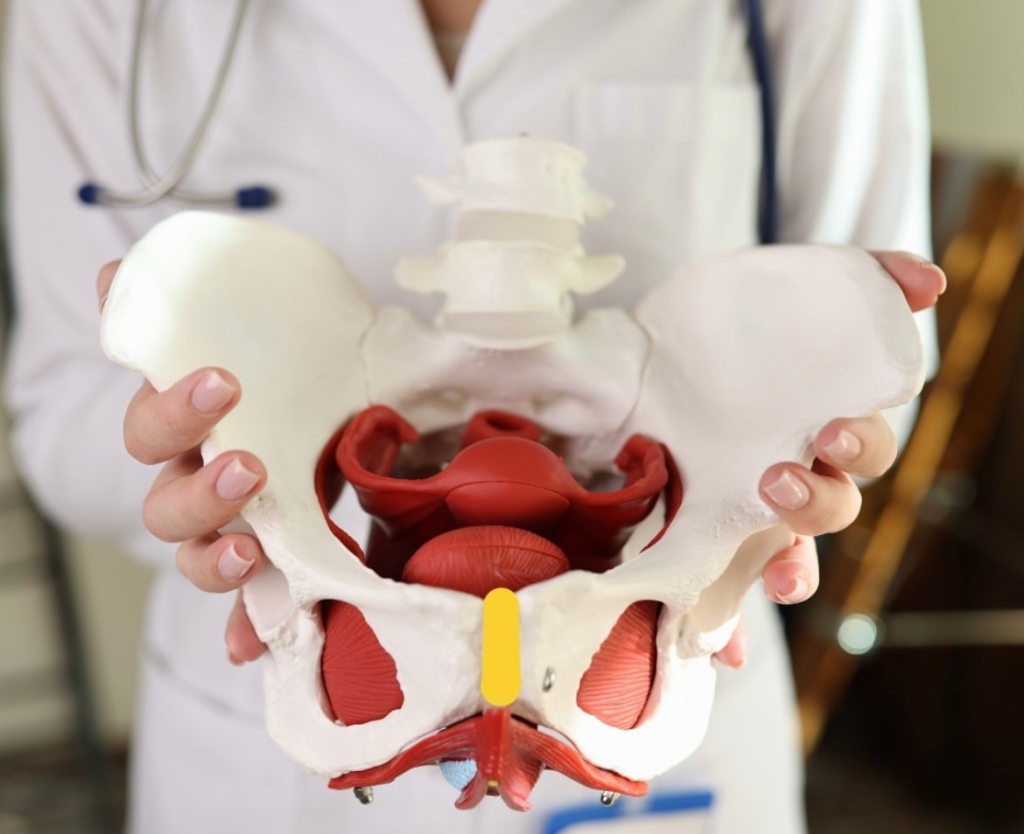
The power of the placenta
There were placentalogists at the workshop—yes, those exist!! And it was amazing to learn how dynamic the placenta is and how it changes throughout pregnancy. The placenta is not just a conduit, its function changes across gestation and with fetal sex and medical condition. It serves as the endocrine function, lungs, pituitary, drug processing center, neuro connections, and growth factors for the baby…to name a few.
For instance, according to this study, there are differing levels of placental chemokines and cytokines and even reduction of placental antibody transfer in male placentas.
Once the placenta is impacted it effects the fetus. There was also discussion about how Inflammatory Bowel Disease impacts placenta—and the possibility of looking at the placenta of an IBD women at delivery to compare them to women without the disease. Even when a woman has well-controlled disease or is in remission, it’s believed our placentas may appear differently at delivery due to the inflammatory nature of our disease. I joked during on one of the speaking panels that I would have gladly given all my placentas to research upon delivery! It’s win-win for researchers and patients alike to do so.

Medication safety in pregnancy
There was also discussion about the importance of developing medications that are safer in pregnancy, much like children’s medications are created with a different formulation.
Prednisone causes minimal fetal exposure. Solumedrol at infusions is fine, and it’s ok to breastfeed on steroids, but high dose daily oral steroid can cause cleft palate and cleft lip.
Azathioprine has also been found to have no impact on breastfeeding, babies born to moms on Azathioprine have normal development and they do not have increased susceptibility to infection.

A graph outlined a study that looked at 107 pregnant women with IBD on Infliximab/Adalimumab:
Detectable anti-TNF levels after birth:
3 months of age—94%
6 months of age—23%
9 months of age—7%
12 months of age—3%
This illustrates why babies exposed to anti-TNF after believed to be immunocompromised until 6 months of age.
Vaccine response and impact of immunosuppressive medications
It is believed that women on immunomodulating medication who get the TDAP vaccination in pregnancy have the same immune response as healthy controls and that the baby receives the same benefits.
The recommendation for Rotavirus (which is the only live vaccine given the first 6 months of a baby’s life), is now to give this vaccine to babies. This updated guidance also applies even when babies are exposed to anti-TNF or immunosuppressive medications in pregnancy.
There’s no difference in vaccine response for babies across different biologics.
Limiting the burden on mom and baby in pregnancy and postpartum studies
Once babies are born and they are part of research studies to measure how their exposure in utero impacts or does not impact their future health, there’s often a burden on the mother about following up. As an IBD mom myself, I wasn’t big on having my babies get blood draws for medical studies—but that data is paramount in helping further that research. And knowing what I know now, I wish I would have been more willing to do so.

So how can studies ease this burden and stress on families?
This can be done by having well-trained phlebotomists who have experience working with children and using techniques to optimize venipuncture success to limit discomfort and pain. By timing blood draws for research at the same time of doctor’s appointments, it reduces the number of needle sticks and blood draws.
Dr. Mahadevan’s Presentation at the workshop
One of my favorite presentations was given by Dr. Uma Mahadevan. She is the key investigator of the PIANO (Pregnancy Inflammatory bowel disease and Neonatal Outcomes), and a well-respected gastroenterologist at UCSF. PIANO started in 2007 and looks at the safety of IBD medications on the pregnancy and short-and-long term outcomes of children. My youngest son is part of PIANO. We participated throughout pregnancy, provided cord blood from delivery, as well as blood draws. I just submitted his 3-year forms online.


I recorded Dr. Mahadevan’s presentation and have transcribed everything she said below so you could hear her expertise firsthand:
“Women of childbearing age—women of reproductive potential are not given JAK inhibitors—even though it may be the most effective medication for them. This is a result of fear—that maybe they’ll get pregnant and maybe there will be some harm. Medications with well-established safety records like anti-TNFs are discontinued in pregnancy now—68% of women who go off their anti-TNF did so from the advice for their rheumatologist, so these are the doctors telling them to do this.
What’s the importance of treating immune mediated disease in pregnancy?
Disease activity is the biggest driver of adverse outcomes in pregnancy. Women with IBD compared to general population have an increased risk of spontaneous abortion, pre-term birth, small for gestational age, hypertensive disorders of pregnancy including preeclampsia , post-partum hemorrhage, and 44% rate of C-section, most of them elective out of fear of disease.
Stopping the biologic which again is out of fear—you’re on a biologic, it’s stopped in pregnancy, still is in many rheumatology and psoriasis cases, less so with IBD, but when you stop it…reducing or stopping leads to an increase of disease flare.
Many of my colleagues who are rheumatologists say “oh many with rheumatoid arthritis get better in pregnancy…there is not a single study that shows that. In fact, this study from The National Inpatient Samples shows women with rheumatoid arthritis were more likely to develop complications of pregnancy both during pregnancy, but also in post-partum and in their neonates.
The American College of Rheumatology conditionally recommended continuing anti-TNF during pregnancy despite the available safety data and the voting panel agreed that if the patient’s disease is under control these medicines can be discontinued. This is happening now.
In this article from a prospective registry from Sweden and Denmark that looked at 1700 patients with RA, there was increase in pre-term birth and small for gestational age in RA compared to the general population and that odds ratio increased to three-fold with active disease.
So, there is data that it increases harm in not just IBD but RA as well. We know there’s a strong role for inflammation in pregnancy and in pregnancy outcomes. So, the significant increase in pregnancy and neonatal complications is closely linked to disease activity and inflammation and stopping these low-risk meds and steroid sparing therapies lead to increased suffering for the mother, and post-partum flares and worst outcomes for the infant.
Healthy mother=Healthy Baby
So, what are some of the study designs and limitations-these have been brought up before. Pregnant women are not included in clinical trials. There’s unmeasured confounding in uncontrolled studies. Disease activity impacts the decision to continue or discontinue therapy. It’s not random. The choice of therapy is not random it is linked to their disease severity and what they have.
If you have a series of 100 patients or 1000 patients or 10,000 patients, you may not pick up the signal. The types of studies that are used for the most part are large data sets, so birds eye view and the highest quality study are large population studies from countries in Scandinavia usually where they have longitudinal assessment, parent-child linkage, and a good assessment of diagnosis in pregnancy outcomes. However, these are limited by a fair assessment of medication because they can only measure prescription and not whether the patient is actually taking the medicine. At a very poor assessment of disease activity and very granular data.
People are more likely to report a complication than a healthy pregnancy—incomplete info.
Let me tell you about PIANO—this is a prospective national registry of pregnant women with IBD started in 2007. PIANO divides people into four groups:
- The unexposed—which could include people on steroids, 5 ASAS, antibiotics.
- Thiopurines: Azathioprine, 6-mercaptop, urine
- Biologics: Infliximab, Adalimumab, Certolizumab, Natalizumab
- Combination Therapy: Azathioprine + Biologic
We define exposure as anytime within 3 months of conception through pregnancy. We compare the offspring of women exposed to a medication to offspring of women with IBD who have not been exposed. We looked at multiple different outcomes including pregnancy and neonatal outcomes , we administered questionnaires each trimester of pregnancy, three times in the first year of birth and then annually and we continue to follow these patients out to age 18.
So, here’s some of the data that has been published:
Corticosteroids –I often hear from providers, “oh I’ll just stop their medication and if they flare, we’ll give them steroids.” This actually leads to increase rates of pre-term birth, low birth weight, and NICU admission. Of course, the use of steroids is mostly tied to disease activity. It’s hard to separate the two. But the whole point is that you don’t want disease activity, you don’t want steroid use, you want them to be on a steroid sparring effective therapy.
The primary results of PIANO were published in 2021 in Gastro. We looked at 1,400 IBD pregnancies, 379 were not on drugs, 242 were on thiopurine, 642 were on biologics (Primarily anti-TNF), and 227 were on both biologic and thiopurines so about 1,000 biologic exposed pregnancies. We found no increase in birth defects, spontaneous abortion, preterm birth, low birth weight, or infections in the first year of life. We saw an increase in spontaneous abortion with disease activity and we used the Ages and Stages questionnaires to look at developmental milestones and saw no reduction.
We measured placental transfer and we measured maternal and cord blood for inflammation on day of birth. The highest transfer was with infliximab—the lowest was certolizumab, which doesn’t have the FC portion. Vedolizumab had a lower level in the infant than the mother. When this data first came out the first reaction was – “oh we should stop the biologic early”…so in Europe they have more of a glass is half empty look at medications in pregnancy…US tends to be glass is half full. So, they decided to stop at 22 weeks and that was in their official guidance. And it was not until 2 years ago that that was changed to match US recommendations because their own data showed an increase in disease activity and worse outcomes with doing that.
The concern was if you have this placental transfer, if you have therapeutic drug levels in the infant for several months after birth, do they have higher rates of infection? And we showed in PIANO there is no increase in infection at 4 months of age and at 1 year and we looked at if infection rates were relative to the level of drug in the infant at the time of birth, and there was no association to drug level at birth and recent infection.
So based on that now, we don’t stop the biologic at all during pregnancy, we continue it throughout. A systematic review and meta-analysis looking at 8,000 women with IBD who were exposed to biologics showed no increase in infant infections, antibiotic—- showing that biologics do not cause harm.
This data from Antoine Meyer who uses a French patient sample looked at women on anti-TNF and thiopurines and showed no increase in the risk of early life malignancy in children.
We ask about infection—we ask about immune suppression—we ask about malignancy and so far in these 3700 thiopurines and 3400 anti-TNFs from 3 years of age going out to 11 years of age, no increase. Very reassuring data.
PIANO looks at developmental milestones—out to 12 months and up to 4 years—shows no decline, we actually showed patients on TNF had statistically superior developmental milestones in every category compared to the national average and even within PIANO—not to say that TNF’s make your kid smarter…but the whole idea of controlling inflammation is what allows these kids to lay down their neural pathways.
What about the newer biologics?
Ustekinumab and Vedolizumab—again showing no increase in harm for both pregnancy and infant outcomes.
Antoine Meyer again from the French database looked at 398 vedolizumab pregnancies, 464 Ustekinumab pregnancies…again, no increase in harm for all these important outcomes.
It’s not just congenital malformations, what else can happen with these medications?
We’re working with Susan Fisher who is a placental scientist at UCSF, a question was raised about Vedolizumab inhibits alpha 4 beta 7, which can inhibit MAdCAM, which is involved in the process of plasmatation—so if you inhibit MAdCAM are you going to have issues in plasmatation. This was just a pilot study. The first one here the patient also had pulmonary hypertension—this is a normal placental at birth…you can see how this looks distinctly abnormal. The second patient was born 39 weeks, mother was completely healthy with her UC had no other issues during pregnancy. Compared to normal placenta…so are there other things we are missing here?
We are conducting a larger study now with multiple biologics the question is it’s not the Vedolizumab is my hypothesis, it’s more a result of inflammation, having IBD…but it will be interesting to see what these placentas look like when we finish. But maybe this is why these patients have higher rates of preeclampsia, higher rates of hypertensive disorders in pregnancy, and preterm birth. It may be related to the impact of inflammation on the placenta.
Small molecules—I feel very comfortable when a new biologic comes out to continue in pregnancy, I feel reassured by the minimal to lack of transfer in the first 14-16 weeks of gestation, with small molecules—they will transfer and Tofacitinib showed teratogenicity at super therapeutic doses, Upadacitinib showed teratogenicity at the doses we use in humans at 30 mg daily—so that does raise concern. There is now some data, again from clinical programs—no increase in birth defects, in pregnancy loss.
Same for –in press—looking at Upadacitinib …128 maternal exposed pregnancies, 80 of which were in clinical trials…similar rates of live births, spontaneous abortion, compared to what is expected.
What about breastmilk? In PIANO, we do collect samples and found the amount of transfer was really miniscule. But all biologics had transfer—we found no increase rates of infection or impact on developmental milestones with patients who were breastfed while the mother was on an immunomodulator.
We talked about vaccines—if these patients had detectable level of biologics—the first 6 months of life will they have normal response to vaccines? We looked at Tetanus — and found the rates of response were similar to infants of mothers who were not exposed to biologics…that was reassuring. We had 40 inadvertent Rotavirus exposures in our TNF babies, they did just fine. This has also been shown in European data as well. And I want to make sure you are all aware of the study from Lancet looking at Rotavirus vaccine—this was a prospective study looking at infants exposed to biologics, they gave 168 biologic exposed infants Rotavirus vaccine—can only be given the first 3-4 months of life, after 6 months it’s not given—so if you say no in the first 6 months, baby never gets it. They found no harm—at this point, we are letting patients on TNF get Rotavirus vaccine, you can argue the US and most areas because of herd immunity, Rotavirus may not be that important, but in other parts of the world it is—and it’s fine to give to patients exposed.
BCG vaccine is different—especially in an anti-TNF exposed baby, it does have a higher rate of TB, having to do with mechanism. There was one death in a European study given vaccine at 1 month of age. BCG can be given after 6 months of age. So Rotavirus is fine within 6 months, but BCG is still recommended after 6 months.
MMR in high-risk populations can be given at 6 months—why did the Europeans, Asians, and Americans have such different guidelines? This May (2024) we all got together for the Global Consensus Conference to create one standard for pregnant women globally and to help spread the word.
Our recommendations are to continue 5ASA, continue sulfasalazine, continue steroids when necessary, stop methotrexate, and continue thiopurine, continue anti-TNF therapy. The US and Europe agree we will not be stopping TNF early, we will continue it on schedule. We’ll continue vedolizumab and ustekinumabon on schedule, and it’s ok to start these medications in the middle of pregnancy.
Biosimilars have equal safety as originator. The Europeans didn’t understand why we wanted to include this, but this is a common question that comes up in the US. We consider biosimilars safety to be equal to the originator drug.
IL-23 therapies… even though not well studied, we feel based on mechanism they can be continued.
Small molecules should be discontinued—but particularly for the JAKS though, unless there is no effective alternative, they can stay on them. I have had patients where they have to stay on Tofacitinib and Upadacitinib because there was nothing else that worked for them.
Inactive vaccines should be given on schedule. we suggest live rotavirus can be given to children exposed to anti-TNF and recommend BCG be avoided in the first six months.
Final thoughts
A recording of this two-day FDA workshop will be available online in the next two weeks. I will share the link as soon as it becomes available. on my Instagram (natalieannhayden). There were fantastic discussions and as an IBD mom who has gone through pregnancies while on a biologic I am grateful for the consideration and the research that’s going on to help couples feel more confident and at ease about bringing life into this world while juggling complicated health conditions. The conversations and presentations at the workshop were extremely complex, I did my best to translate the information, so the patient community has a better grasp of where we stand about IBD pregnancy research.


If you have IBD and are planning to be a mom or if you are currently pregnant, please consider joining the PIANO study and being a part of this life-changing research for our community.